The Ultimate 2026 Guide to Linux Server Security: Hardening Your Infrastructure Against Modern Threats
In the digital landscape of 2026, cybersecurity is no longer an optional add-on; it is the foundation of every successful online venture. As AI-driven brute-force attacks and sophisticated zero-day exploits become more common, maintaining a standard “out-of-the-box” configuration for your VPS or Dedicated server is a recipe for disaster. This Linux Server Security 2026 guide will walk you through the essential steps to transform your server into an impenetrable fortress.
At SarvHost, we provide the raw, enterprise-grade hardware, but the final layer of defense lies in how you configure your environment. Whether you are hosting a high-stakes trading bot in Frankfurt or a private database in New York, these steps are mandatory for professional operations in 2026.
1. Transitioning to SSH Key-Based Authentication
The first and most critical step in Linux Server Security 2026 is the total elimination of password-based logins. Passwords, no matter how complex, are vulnerable to sophisticated phishing and high-speed brute-force attacks.
SSH Keys provide a much higher level of security because they are nearly impossible to decipher by brute force. By generating a 4096-bit RSA key pair or an Ed25519 key, you ensure that only your specific physical machine can initiate a connection to your SarvHost server.
# Generate a secure key on your local machine
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "admin@sarvhost-client"
# Push the key to your server
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub root@your_server_ip2. Hardening the SSH Daemon Configuration
Once your keys are in place, you must lock the “front door.” Modern bots in 2026 scan port 22 relentlessly. To mitigate this, we modify the sshd_config file.
- Change the Default Port: Moving from port 22 to a random high-range port (e.g., 2244) reduces automated scan noise by up to 95%.
- Disable Root Login: Always log in as a standard user with
sudoprivileges. - Disable Password Authentication: Ensure only keys are allowed.
# Edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Port 2244
PermitRootLogin no
PasswordAuthentication no
PubkeyAuthentication yes
3. Implementing a Proactive Firewall with UFW and NFTables
A server without a properly configured firewall is exposed to every vulnerability. In 2026, we utilize the Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) as a frontend for NFTables to manage incoming and outgoing traffic strictly.
The philosophy is simple: Deny everything by default, allow only what is necessary.
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw default allow outgoing
sudo ufw allow 2244/tcp # Your custom SSH port
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp # HTTP
sudo ufw allow 443/tcp # HTTPS
sudo ufw enable4. Intrusion Prevention: Fail2Ban in the AI Era
Even with a custom port, persistent attackers will eventually find your SSH service. Fail2Ban acts as an automated security guard. It monitors system logs for repeated failed login attempts and instantly bans the offending IP address at the firewall level.
In this Linux Server Security 2026 setup, we recommend aggressive banning policies. If an IP fails to log in three times, it should be banned for at least 24 hours to discourage botnets.
5. Kernel Hardening via Sysctl Optimizations
Security isn’t just about ports and passwords; it’s about how the operating system handles data at the network layer. By tweaking the /etc/sysctl.conf file, you can protect your SarvHost VPS against common attacks like IP spoofing and SYN floods.
# IP Spoofing protection
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 1
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1
# Ignore ICMP broadcast requests (Prevents Smurf attacks)
net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_broadcasts = 1
# Protect against SYN flood attacks
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 16. Automated Security Patching: The “Set and Forget” Defense
Many servers are compromised because administrators forget to install security patches for months. In 2026, the unattended-upgrades package is a lifesaver. It automatically installs security updates without requiring manual intervention.
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades
sudo dpkg-reconfigure --priority=low unattended-upgradesThis ensures that as soon as a vulnerability is patched in the Linux community, your server is protected within hours.
7. Monitoring and Audit Logs
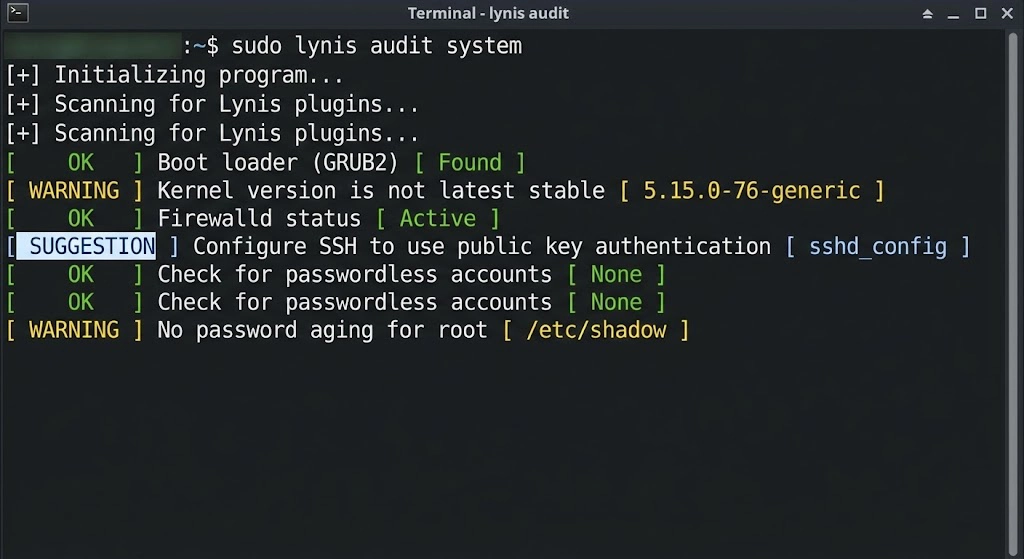
A secure server is a monitored server. Regularly checking your logs is essential for detecting unauthorized access attempts that managed to bypass your initial defenses. Tools like Logwatch or Lynis can provide daily security audits sent directly to your email.
Conclusion: Building a Culture of Security
Applying the steps in this Linux Server Security 2026 guide moves you from being a target to being a fortress. Security is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. By combining these hardening techniques with SarvHost’s premium NVMe infrastructure, you ensure that your projects remain online and your data remains private.
Ready to deploy your next high-security node? Explore our Dedicated Servers and VPS plans today. Use code WELCOME2026 for a 25% lifetime discount.
👉 Secure Your Future with SarvHost.net